Navigating the world of student loans can be overwhelming, but it is essential for financing your education. With so many options available, it’s important to make an informed decision to ensure that you are borrowing the right amount, at the right terms, and with the best interest rates. In this guide, we’ll explore how to choose the right student loan for your needs, from federal loans to private lenders, and everything in between. By understanding the different types of loans, their benefits, and how they align with your educational goals, you can set yourself up for success both during and after graduation.
1. Start with Federal Student Loans
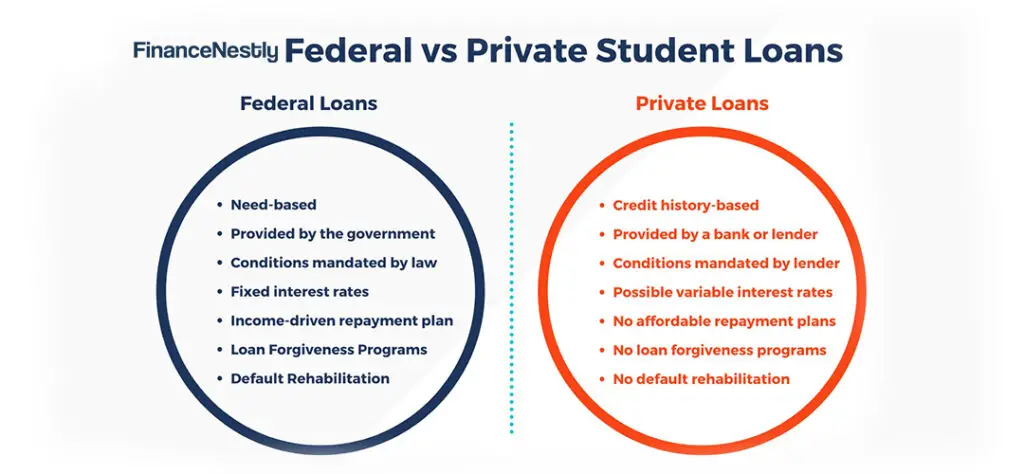
The first step when considering student loans is to explore federal loan options. Federal loans are generally the best option for most students, as they offer fixed interest rates, flexible repayment plans, and various borrower protections that private loans cannot match. These include deferment, forbearance, and income-driven repayment options.
There are two main types of federal student loans: Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans. Direct Subsidized Loans are available to undergraduate students who demonstrate financial need, and the government pays the interest while you’re in school. On the other hand, Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students, but you are responsible for the interest from the moment the loan is disbursed.
Before looking into private loans, be sure to max out your eligibility for federal loans, as they typically offer lower interest rates and more favorable repayment terms. If you need additional funds after exhausting federal loan options, consider private student loans. For more information on the differences between federal and private loans, check out this comparison guide.
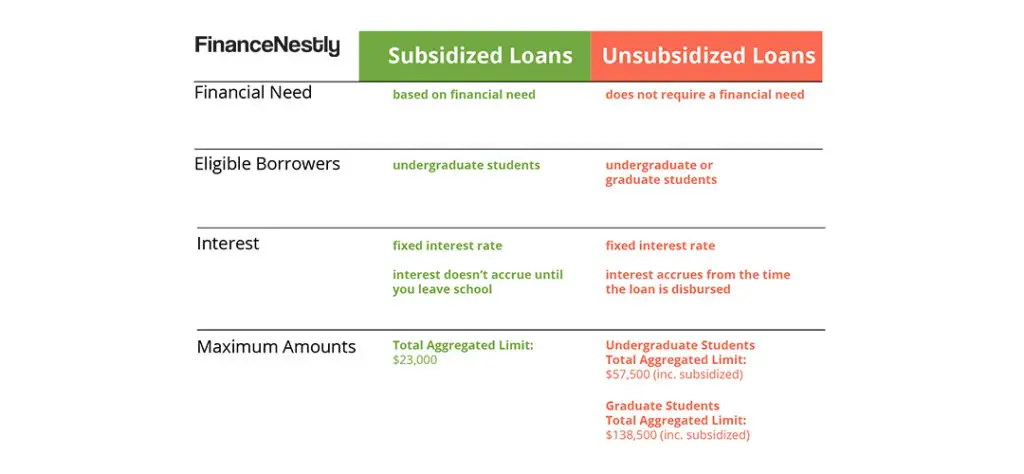
2. Understand the Interest Rates and Repayment Terms
The interest rate on your student loan will have a significant impact on the total amount you repay over the life of the loan. Federal loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to private loans. For federal loans in 2024, the interest rates are fixed, meaning they won’t change over time. Private loans, however, can offer either fixed or variable rates, and these rates often depend on your credit history and the lender’s terms.
When selecting a loan, it’s important to consider the repayment terms. Federal student loans offer more flexible repayment options, such as income-driven repayment (IDR) plans, which adjust your monthly payments according to your income level. Private loans, however, may have less flexibility in terms of repayment, and missing payments could result in penalties or an increase in the interest rate.
To compare interest rates and repayment terms, visit this student loan comparison tool, which allows you to see a breakdown of various loan types and lenders.
3. Consider Private Loans for Additional Funding
While federal student loans should be your first choice, private student loans can help bridge the gap if you need additional funding for your education. Private loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders, and they often require a credit check. Unlike federal loans, private loans may have variable interest rates that fluctuate based on the market, which can lead to either higher or lower rates over time.
If you are considering a private student loan, make sure to shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders to secure the best rate. Additionally, consider whether the lender offers any borrower protections, such as deferment or forbearance in case of financial hardship. If you have a co-signer with good credit, it may help you secure a better interest rate on a private loan.
Before taking out a private loan, make sure you fully understand the terms and conditions. Private loans can be more expensive than federal loans, and they may come with fewer repayment options.
4. Evaluate Your Expected Income After Graduation
One of the key factors in choosing the right student loan is evaluating your future income potential. Before taking on any loan, especially a large one, it’s important to consider how much money you expect to earn after graduation and how long it will take you to repay the loan.
If you’re entering a field with a high earning potential, you may be able to afford a larger loan with a higher interest rate. Conversely, if you’re pursuing a degree in a field with lower average salaries, you may want to opt for a loan with more favorable repayment terms to avoid financial strain after graduation.
Additionally, consider whether the loan offers any income-driven repayment options that can adjust based on your earnings after graduation. The ability to change your monthly payments based on your income can provide flexibility if you find yourself in a financial bind.
For a clearer picture of potential salaries by major, refer to this salary projection tool.
5. Look for Loan Forgiveness Programs
Another important consideration when choosing a student loan is whether it qualifies for loan forgiveness programs. Federal student loans, especially those for public service workers, offer several loan forgiveness options, such as the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program. This program forgives the remaining balance of your loan after you make 120 qualifying monthly payments while working for a government or non-profit organization.
If you are pursuing a career in education, healthcare, or a similar field, be sure to research the loan forgiveness programs available to you. Loan forgiveness can significantly reduce the burden of student loan debt, but it is essential to follow the specific requirements of the program.
Private loans, however, generally do not offer loan forgiveness options. If you are relying on forgiveness as part of your repayment strategy, it may be wise to limit the amount of private loans you take on.
Conclusion
Choosing the right student loan is crucial to securing the best financial future for your education. Start by exploring federal loans, as they offer the best interest rates, repayment flexibility, and borrower protections. Then, if necessary, look into private loans for additional funding but ensure you carefully compare interest rates and terms. Ultimately, choose a loan that aligns with your career goals, repayment capabilities, and financial situation. With the right planning and understanding, you can make a loan decision that minimizes debt and helps you achieve academic success.

