Introduction: A New Era of Money
Cryptocurrencies have emerged as one of the most transformative innovations in finance over the past decade. These digital currencies, powered by blockchain technology, promise to revolutionize how we think about money, payments, and economic systems. As central banks explore digital alternatives and decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum gain traction, understanding their economic implications is critical.
This blog delves into the rise of cryptocurrencies, their potential benefits, challenges, and what they mean for the global economy.
What Are Cryptocurrencies?
Defining Digital Currencies
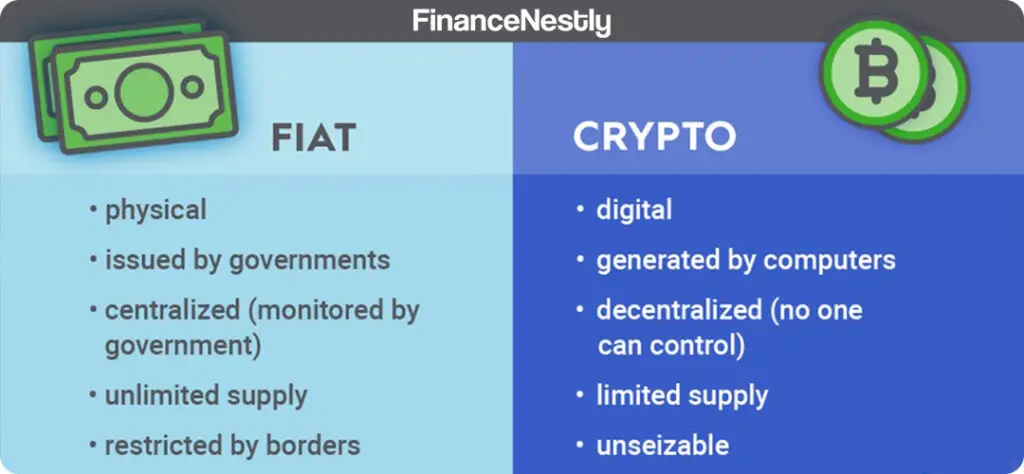
Cryptocurrencies are decentralized digital assets that use cryptography to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Unlike traditional fiat currencies, they operate on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Key Features
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the currency.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology records all transactions in a public ledger.
- Borderless: Transactions can occur globally without intermediaries.
Examples of Popular Cryptocurrencies
- Bitcoin: The first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum: A blockchain platform that supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the US dollar to reduce volatility.
The Economic Implications of Cryptocurrencies
1. Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies provide access to financial services for the unbanked and underbanked populations, particularly in developing regions. With only a smartphone and internet connection, individuals can participate in the global economy.
2. Redefining Monetary Policy
Decentralized cryptocurrencies challenge traditional monetary systems. Central banks are responding with Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), which blend the advantages of digital currencies with government oversight.
3. Cross-Border Transactions
Cryptocurrencies streamline international payments by reducing reliance on traditional banking systems and lowering transaction fees. This is particularly impactful for remittances.
4. Speculation and Market Volatility
Cryptocurrencies have introduced new opportunities for investment but are notorious for their volatility. Speculative trading can lead to economic instability if not properly managed.
Benefits and Risks of Cryptocurrencies
Benefits
- Transparency and Security: Blockchain ensures data integrity and reduces fraud.
- Efficiency: Faster and cheaper transactions compared to traditional systems.
- Innovation: Supports decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling new financial products and services.
Risks
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies.
- Energy Consumption: Mining and transaction verification consume significant energy resources.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacks.
The Role of Governments and Regulation
Current Regulatory Landscape
Countries like the US and the EU are working on frameworks to regulate cryptocurrencies, balancing innovation with consumer protection. Meanwhile, some nations, such as El Salvador, have embraced Bitcoin as legal tender.
The Case for CBDCs
Central Bank Digital Currencies aim to combine the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability of traditional systems. CBDCs can enhance payment systems, reduce cash dependency, and combat illicit activities.
Taxation and Compliance
As cryptocurrency adoption grows, tax authorities worldwide are implementing policies to track and tax digital asset transactions, ensuring that the system remains sustainable.
Conclusion: The Future of Money
Digital currencies are reshaping the financial landscape, offering unparalleled opportunities and challenges. Cryptocurrencies have already disrupted traditional systems, paving the way for innovative solutions to age-old economic issues. However, as adoption accelerates, collaboration between stakeholders—governments, businesses, and consumers—is essential to ensure that this new era of money fosters global economic growth and stability.

