Introduction: Understanding the World’s Largest Financial Market
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is the process of buying and selling currencies to profit from changes in their values. With a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, the forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. But how does it work, and why has it become a focal point for traders globally?
This blog will break down the basics of forex trading, explain its mechanics, and highlight what makes it a unique and dynamic market.
What Is Forex Trading?
The Basics of Forex Trading
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another. These transactions occur in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). Each pair has a base currency (the first) and a quote currency (the second). For instance, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.10, it means 1 Euro equals 1.10 US Dollars.
The Key Players in Forex
- Central Banks: Major influencers through monetary policy decisions.
- Commercial Banks: Facilitate the majority of forex transactions.
- Retail Traders: Individuals participating through online trading platforms.
- Corporations: Use forex to hedge against currency risk in international trade.
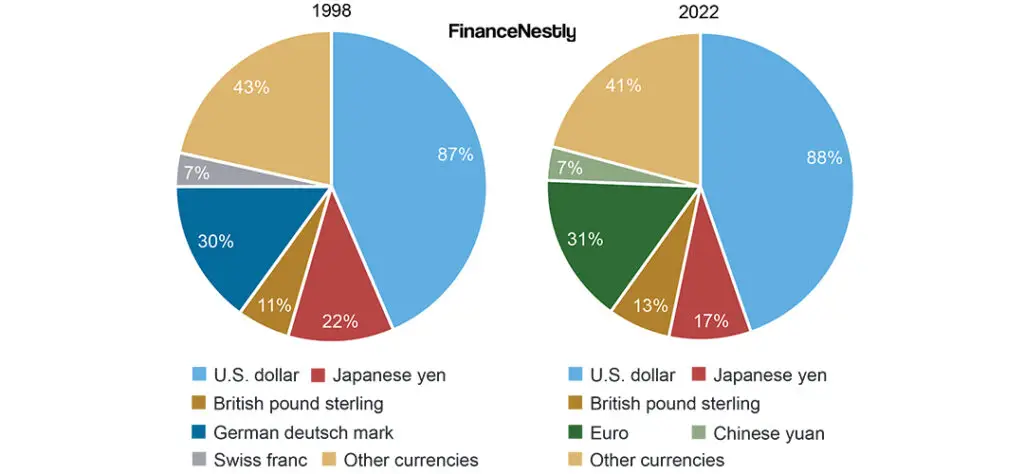
How Does Forex Trading Work?
1. The Market Structure
The forex market operates as a decentralized global network, open 24 hours a day, five days a week. Trading begins in Sydney, moves to Tokyo, then London, and finally New York, ensuring seamless activity across time zones.
2. Types of Forex Markets
- Spot Market: Immediate currency exchanges based on current prices.
- Forward Market: Agreements to trade currencies at a future date and set price.
- Futures Market: Standardized contracts traded on exchanges for future delivery.
3. Trading Mechanisms
Forex trading is conducted via brokers or trading platforms. Traders speculate on currency movements by either buying (going long) or selling (going short). Leverage—borrowing funds to increase trading power—is commonly used but comes with significant risk.

Why Trade Forex?
Advantages
- High Liquidity: Trillions of dollars traded daily ensure fast transactions and tight spreads.
- Accessibility: Online platforms allow anyone with an internet connection to trade.
- Leverage Opportunities: Small capital can control large positions, amplifying potential profits.
Risks
- Volatility: Sharp price changes can result in significant losses.
- Leverage Risks: While leverage can magnify gains, it equally increases potential losses.
- Lack of Regulation: Forex trading is less regulated compared to other financial markets, especially for retail traders.
Forex Trading Strategies
1. Day Trading
Traders open and close positions within the same day, aiming to profit from short-term price movements.
2. Swing Trading
Positions are held for several days or weeks to capitalize on medium-term trends.
3. Hedging
Investors use forex to protect against unfavorable currency fluctuations, especially in international business transactions.
4. Scalping
This strategy involves making multiple small trades to profit from minute price changes over a short period.
Conclusion: Is Forex Trading Right for You?
Forex trading offers immense opportunities for profit, but it requires a deep understanding of the market, disciplined strategies, and effective risk management. Whether you’re looking to diversify your investment portfolio or explore a new financial venture, forex trading can be rewarding if approached with caution and preparation. As the saying goes, knowledge is power—especially in the fast-paced world of forex.

